MultipleShearSpring Element
- Command_Manual
- Tcl Commands
- Modeling_Commands
- model
- uniaxialMaterial
- ndMaterial
- frictionModel
- section
- geometricTransf
- element
- node
- sp commands
- mp commands
- timeSeries
- pattern
- mass
- block commands
- region
- rayleigh
- Analysis Commands
- Output Commands
- Misc Commands
- DataBase Commands
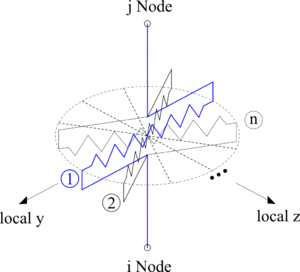
This command is used to construct a multipleShearSpring (MSS) element object, which is defined by two nodes. This element consists of a series of identical shear springs arranged radially to represent the isotropic behavior in the local y-z plane.
| element multipleShearSpring $eleTag $iNode $jNode $nSpring -mat $matTag <-lim $dsp> <-orient <$x1 $x2 $x3> $yp1 $yp2 $yp3> <-mass $m> |
| $eleTag | unique element object tag |
| $inode $jnode | end nodes |
| $nSpring | number of springs |
| $matTag | tag associated with previously-defined UniaxialMaterial object |
| $dsp | minimum deformation to calculate equivalent coefficient (see note 1) |
| $x1 $x2 $x3 | vector components in global coordinates defining local x-axis |
| $yp1 $yp2 $yp3 | vector components in global coordinates defining vector yp which lies in the local x-y plane for the element |
| $m | element mass |
NOTES:
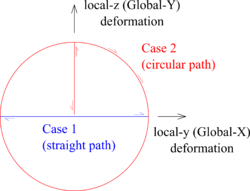
1) If $dsp is positive and the shear deformation of MSS exceeds $dsp, this element calculates equivalent coefficient to adjust force and stiffness of MSS. The adjusted MSS force and stiffness reproduce the behavior of the previously defined uniaxial material under monotonic loading in every direction. If $dsp is zero, the element does not calculate the equivalent coefficient.
2) The valid queries to a multipleShearSpring element when creating an ElementRecorder object are 'globalForce', 'localForce', 'basicForce', 'localDisplacement' and 'basicDeformation'.
EXAMPLE:
element multipleShearSpring 1 1 2 16 -mat 1
MultipleShearSpring_Sample.tcl, MultipleShearSpring_input_X.tcl, MultipleShearSpring_input_Y.tcl
REFERENCES:
Wada. A. and Hirose K. , "Building Frames Subjected to 2D Earthquake Motion", Seismic Engineering: Research and Practice, American Society of Civil Engineers, 388-397, 1989.
Code Developed by: mkiku