ElastomericX: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Manishkumar (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Manishkumar (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
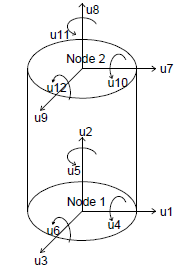
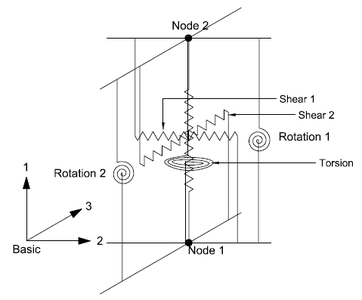
This command is used to construct an ElastomericX bearing element object. The 3D continuum geometry of an elastomeric bearing is modeled as a 2-node, 12 DOF discrete element. | This command is used to construct an ElastomericX bearing element object in three-dimension. The 3D continuum geometry of an elastomeric bearing is modeled as a 2-node, 12 DOF discrete element. This elements extends the formulation of [[Elastomeric_Bearing_(Plasticity)_Element]] (or [[Elastomeric_Bearing_(Bouc-Wen)_Element]]) elements, however instead of an user providing material models as input arguments, it only takes geometric and material properties of an elastomeric bearing as arguments. The material models in six direction are formulated within the element from input arguments. | ||
[[ | |||
[[File:Elastomeric3DModel.png|x300px|border|inline|Physical continuum model]] [[File:ElastomericDiscreteSpring.png|x300px|border|inline|Discrete spring representation]] | |||
Revision as of 02:33, 24 May 2014
This command is used to construct an ElastomericX bearing element object in three-dimension. The 3D continuum geometry of an elastomeric bearing is modeled as a 2-node, 12 DOF discrete element. This elements extends the formulation of Elastomeric_Bearing_(Plasticity)_Element (or Elastomeric_Bearing_(Bouc-Wen)_Element) elements, however instead of an user providing material models as input arguments, it only takes geometric and material properties of an elastomeric bearing as arguments. The material models in six direction are formulated within the element from input arguments.