UVCuniaxial (Updated Voce-Chaboche): Difference between revisions
A.Hartloper (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
A.Hartloper (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
Available in OpenSees version 3.1.0+. | Available in OpenSees version 3.1.0+. | ||
Updated in OpenSees version 3.4.0+ (05-Jul-2022). | |||
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 91: | Line 92: | ||
The RESSPyLab package can be used to generate UVC model parameters for other steel materials if the data is available. | The RESSPyLab package can be used to generate UVC model parameters for other steel materials if the data is available. | ||
Details and examples on the calibration are provided on the [https://pypi.org/project/RESSPyLab/ RESSPyLab] web page. | Details and examples on the calibration are provided on the [https://pypi.org/project/RESSPyLab/ RESSPyLab] web page. | ||
Note that the parameters provided in the table below were calibrated using the true stress-strain definition, i.e., e_true = ln(1+(L-L_0)/L_0) and s_true = F/A_0 * (1 + (L-L_0)/L_0). | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 130: | Line 133: | ||
Please use Reference [1] when citing the UVC model. | Please use Reference [1] when citing the UVC model. | ||
'''[1]''' Hartloper, A. R., de Castro e Sousa A., and Lignos D.G. "Constitutive Modeling of Structural Steels: | '''[1]''' Hartloper, A. R., de Castro e Sousa A., and Lignos D.G. "Constitutive Modeling of Structural Steels: Nonlinear Isotropic/Kinematic Hardening Material Model and its Calibration", https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0002964. | ||
'''[2]''' Hartloper, A. R., de Castro e Sousa A., and Lignos D.G. (2019). "Sensitivity of Simulated Steel Column Instabilities to Plasticity Model Assumptions". 12th Canadian Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Quebec City, QC, Canada. https://infoscience.epfl.ch/record/267788 | '''[2]''' Hartloper, A. R., de Castro e Sousa A., and Lignos D.G. (2019). "Sensitivity of Simulated Steel Column Instabilities to Plasticity Model Assumptions". 12th Canadian Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Quebec City, QC, Canada. https://infoscience.epfl.ch/record/267788 | ||
Latest revision as of 20:04, 5 July 2022
- Command_Manual
- Tcl Commands
- Modeling_Commands
- model
- uniaxialMaterial
- ndMaterial
- frictionModel
- section
- geometricTransf
- element
- node
- sp commands
- mp commands
- timeSeries
- pattern
- mass
- block commands
- region
- rayleigh
- Analysis Commands
- Output Commands
- Misc Commands
- DataBase Commands
This command is used to construct an Updated Voce-Chaboche (UVC) material for uniaxial stress states (e.g., beam elements). This material is a refined version of the classic nonlinear isotropic/kinematic hardening material model based on the Voce isotropic hardening law and the Chaboche kinematic hardening law. The UVC model contains an updated isotropic hardening law, with parameter constraints, to simulate the permanent decrease in yield stress with initial plastic loading associated with the discontinuous yielding phenomenon in mild steels.
Details regarding the model, its implementation, and calibration can be found in the references cited at the end. The multiaxial (e.g., for solid/brick elements) and plane-stress (e.g., for quad/plate/shell elements) versions are also available. The multiaxial and plane-stress implementations have the exact same hardening rules as this uniaxial model, and only differ in their purpose and numerical implementation.
Available in OpenSees version 3.1.0+. Updated in OpenSees version 3.4.0+ (05-Jul-2022).
| uniaxialMaterial UVCuniaxial $matTag $E $fy $QInf $b $DInf $a $N $C1 $gamma1 <$C2 $gamma2 $C3 $gamma3 … $C8 $gamma8> |
| $matTag | Integer tag identifying the material. |
| $E | Elastic modulus of the steel material. |
| $fy | Initial yield stress of the steel material. |
| $QInf | Maximum increase in yield stress due to cyclic hardening (isotropic hardening). |
| $b | Saturation rate of QInf, b > 0. |
| $DInf | Decrease in the initial yield stress, to neglect the model updates set DInf = 0. |
| $a | Saturation rate of DInf, a > 0. If DInf == 0, then a is arbitrary (but still a > 0). |
| $N | Number of backstresses to define, N >= 1. |
| $C1 | Kinematic hardening parameter associated with backstress component 1. |
| $gamma1 | Saturation rate of kinematic hardening associated with backstress component 1. |
| <$C2 $gamma2 $C3 $gamma3 … $C8 $gamma8> | Additional backstress parameters, up to 8 may be specified. If C is specified, then the corresponding gamma must also be specified. Note that only the first N backstresses will be read by the parser. |
Examples
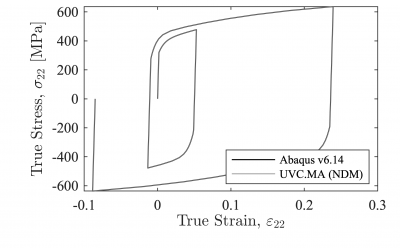
1. Validation with Abaqus:
This first example compares the response of the UVC model with the built-in nonlinear isotropic/kinematic material model in Abaqus v6.14. For this validation the model updates are neglected by simply setting DInf = 0.0 and a = 1.0. The model parameters are:
E = 179800 MPa, fy = 318.5 MPa, QInf = 100.7 MPa, b = 8.0, DInf = 0.0 MPa, a = 1.0, C1 = 11608.2 MPa, gamma1 = 145.2, C2 = 1026.3 MPa, gamma2 = 4.7
Figure 1 shows that the UVC implementation in OpenSees agrees with the built-in Abaqus model to the level of machine precision. Therefore, you can use the UVC model in place of the nonlinear isotropic/kinematic hardening material model provided in Abaqus and many other finite element simulation platforms. The finite element models used to validate the Abaqus and OpenSees responses can be found at https://github.com/ahartloper/UVC_MatMod.
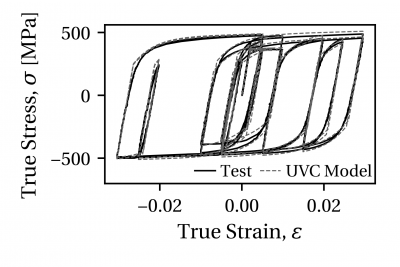
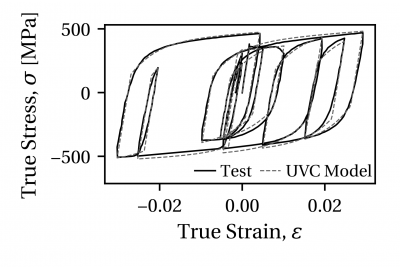
2. Comparison with structural steels:
The applicability of the UVC material model for structural steels is demonstrated through two comparisons with experimental data from uniaxial coupon tests. A comparison with a North American steel, A992 Gr. 50 (nominal fy = 345 MPa), is shown in Figure 2. A comparison with a European steel, S355J2+N (nominal fy = 355 MPa), is shown in Figure 3. In both cases the UVC model is able to represent well the initial yield stress as well as the material behavior in later loading cycles.
The parameters used for the A992 Gr. 50 and S355J2+N steels, along with other common structural steels, are provided and discussed in the next section.
-
Figure 2. Comparison of UVC model with uniaxial coupon test data from the A992 Gr. 50 W14X82 flange data set.
-
Figure 3. Comparison of UVC model with uniaxial coupon test data from the S355J2+N 25 mm plate data set.
UVC model parameters for structural steels
Below is a list of UVC model parameters for twelve structural steels from Reference [1] using two backstresses. These parameters are applicable for all implementations of the UVC model (uniaxial, plane-stress, multiaxial).
References [1,3] contain detailed information on the calibration procedure used to obtain the model parameters. All of the parameters provided in the table below were obtained by minimizing the total squared-strain energy across at least five uniaxial coupon tests of distinct strain histories subject to the constraint that the material response is non-softening. Therefore, the UVC material model parameters should be representative of steel material behavior for arbitrarily imposed strains. Note that although the parameters in this table are considered representative of a specific sample of each material, significant variations can exist between different samples of the same material.
All the parameters in the table are obtained through the UVC model calibration procedure implemented in the open-source Python package RESSPyLab. The RESSPyLab package can be used to generate UVC model parameters for other steel materials if the data is available. Details and examples on the calibration are provided on the RESSPyLab web page.
Note that the parameters provided in the table below were calibrated using the true stress-strain definition, i.e., e_true = ln(1+(L-L_0)/L_0) and s_true = F/A_0 * (1 + (L-L_0)/L_0).
| UVC Material Parameters | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | E | fy | QInf | b | DInf | a | C1 | gamma1 | C2 | gamma2 |
| - | [GPa] | [MPa] | [MPa] | - | [MPa] | - | [MPa] | - | [MPa] | - |
| S355J2+N (25 mm plate) | 197.41 | 338.80 | 134.34 | 14.71 | 133.75 | 229.25 | 26242.00 | 199.04 | 2445.30 | 11.66 |
| S355J2+N (50 mm plate) | 185.97 | 332.18 | 120.48 | 8.14 | 93.15 | 261.75 | 21102.00 | 173.60 | 2300.60 | 10.42 |
| S355J2+N (HEB500 flange) | 192.13 | 315.04 | 138.01 | 11.36 | 96.16 | 223.66 | 18587.84 | 257.31 | 1351.98 | 6.52 |
| S355J2+N (HEB500 web) | 199.68 | 334.94 | 139.32 | 14.07 | 120.33 | 274.73 | 28528.03 | 315.17 | 2569.45 | 24.68 |
| S460NL (25 mm plate) | 187.61 | 439.20 | 97.35 | 14.02 | 136.64 | 226.40 | 26691.00 | 188.75 | 2892.40 | 10.44 |
| S690QL (25 mm plate) | 188.63 | 685.39 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 132.30 | 285.15 | 34575.00 | 185.16 | 3154.20 | 20.14 |
| A992 Gr. 50 (W14X82 web) | 210.74 | 378.83 | 122.63 | 19.74 | 143.49 | 248.14 | 31638.00 | 277.32 | 1548.60 | 9.04 |
| A992 Gr. 50 (W14X82 flange) | 191.02 | 373.72 | 141.47 | 15.20 | 135.95 | 211.16 | 25621.00 | 235.12 | 942.18 | 3.16 |
| A500 Gr. B (HSS305X16) | 191.21 | 324.09 | 228.02 | 0.11 | 50.41 | 270.40 | 17707.00 | 207.18 | 1526.20 | 6.22 |
| BCP325 (22 mm plate) | 178.61 | 368.03 | 112.25 | 10.78 | 105.95 | 221.92 | 20104.00 | 200.43 | 2203.00 | 11.76 |
| BCR295 (HSS350X22) | 178.74 | 412.21 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 103.30 | 212.83 | 20750.59 | 225.26 | 1245.04 | 2.09 |
| HYP400 (27mm plate) | 189.36 | 454.46 | 62.63 | 16.57 | 109.28 | 145.74 | 13860.00 | 141.61 | 1031.10 | 3.53 |
References:
Please use Reference [1] when citing the UVC model.
[1] Hartloper, A. R., de Castro e Sousa A., and Lignos D.G. "Constitutive Modeling of Structural Steels: Nonlinear Isotropic/Kinematic Hardening Material Model and its Calibration", https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0002964.
[2] Hartloper, A. R., de Castro e Sousa A., and Lignos D.G. (2019). "Sensitivity of Simulated Steel Column Instabilities to Plasticity Model Assumptions". 12th Canadian Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Quebec City, QC, Canada. https://infoscience.epfl.ch/record/267788
[3] Hartloper, A. R., de Castro e Sousa A., and Lignos D.G. (2019). "A Nonlinear Isotropic/Kinematic Hardening Model for Materials with Discontinuous Yielding". Report No. 271062, Resilient Steel Structures Laboratory (RESSLab), EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerland. https://infoscience.epfl.ch/record/271062.
Code developed, implemented, and maintained by: Alex Hartloper (EPFL). Issues, bugs, and feature requests can be opened at the github repository.