BilinearOilDamper Material: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{CommandManualMenu}} | {{CommandManualMenu}} | ||
This command is used to construct a BilinearOilDamper material, which simulates the hysteretic response of bilinear oil dampers with | This command is used to construct a BilinearOilDamper material, which simulates the hysteretic response of bilinear oil dampers with relief valve. Two adaptive iterative algorithms have been implemented and validated to solve numerically the constitutive equations within a bilinear oil damper with a high-precision accuracy. | ||
{| | {| | ||
| style="background:lime; color:black; width:800px" | '''uniaxialMaterial BilinearOilDamper $matTag $K $Cd | | style="background:lime; color:black; width:800px" | '''uniaxialMaterial BilinearOilDamper $matTag $K $Cd <$Fr $p> <$LGap> < $NM $RelTol $AbsTol $MaxHalf> ''' | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
| style="width:150px" | '''$matTag ''' || integer tag identifying material | | style="width:150px" | '''$matTag ''' || integer tag identifying material | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''$K ''' || Elastic stiffness of linear spring | | '''$K ''' || Elastic stiffness of linear spring to model the axial flexibility of an oil damper (brace and damper portion) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''$Cd ''' || Viscous | | '''$Cd ''' || Viscous damping coefficient of an oil damper (before relief) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | '''$Fr ''' || Damper relief load (default=1.0, Damper property) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''$p ''' || Post-relief viscous damping coefficient ratio (default=1.0, linear oil damper) | |||
| '''$p ''' || Post-relief damping coefficient ratio ( | |||
|- | |- | ||
| '''$LGap ''' || gap length to simulate the gap length due to the pin tolerance | | '''$LGap ''' || gap length to simulate the gap length due to the pin tolerance (default=0.0: zero tolerance) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''$NM ''' || Employed adaptive numerical algorithm (default value NM = 1; 1 = Dormand-Prince54, 2=adaptive finite difference) | | '''$NM ''' || Employed adaptive numerical algorithm (default value NM = 1; 1 = Dormand-Prince54, 2=adaptive finite difference) | ||
| Line 28: | Line 26: | ||
| '''$RelTol ''' || Tolerance for absolute relative error control of the adaptive iterative algorithm (default value 10^-6) | | '''$RelTol ''' || Tolerance for absolute relative error control of the adaptive iterative algorithm (default value 10^-6) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''$AbsTol ''' || Tolerance for absolute error control of adaptive iterative algorithm (default value 10^- | | '''$AbsTol ''' || Tolerance for absolute error control of adaptive iterative algorithm (default value 10^-10) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''$MaxHalf ''' || Maximum number of sub-step iterations within an integration step (default value 15) | | '''$MaxHalf ''' || Maximum number of sub-step iterations within an integration step (default value 15) | ||
| Line 43: | Line 41: | ||
|- | |- | ||
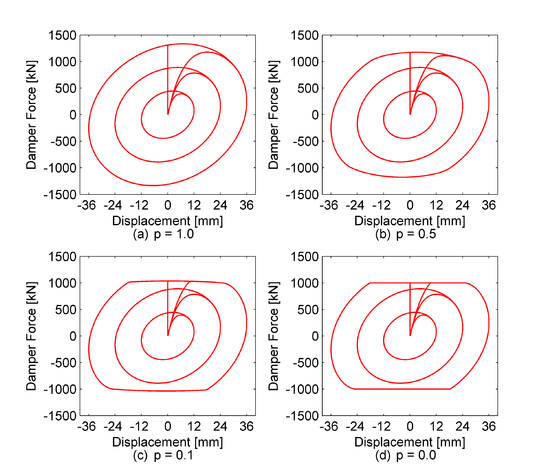
| Assume a bilinear oil damper with axial stiffness K=200.0kN/mm, viscous damping coefficient C=6.0KN/(mm/s), relief load Fr=1000.0KN, p=0.1. | | Assume a bilinear oil damper with axial stiffness K=200.0kN/mm, viscous damping coefficient C=6.0KN/(mm/s), relief load Fr=1000.0KN, p=0.1. | ||
|- | |||
| The input parameters for the material should be as follows: | | The input parameters for the material should be as follows: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 53: | Line 51: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File: | | [[File:BOD_1.png|550px|thumb|left| Figure 1.Oil Damper with various post-relief viscous damping coefficient ratios]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
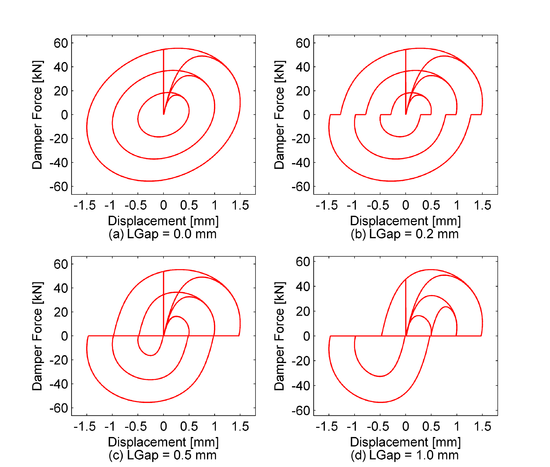
| Assume a bilinear oil damper with axial stiffness K=200.0kN/mm, viscous damping coefficient C=6.0KN/(mm/s), relief load Fr=1000.0KN, p=0.1 and LGap = 0.5mm due to the pin tolerance at the damper ends. | | Assume a bilinear oil damper with axial stiffness K=200.0kN/mm, viscous damping coefficient C=6.0KN/(mm/s), relief load Fr=1000.0KN, p=0.1 and LGap = 0.5mm due to the pin tolerance at the damper ends. | ||
|- | |||
| The input parameters for the material should be as follows: | | The input parameters for the material should be as follows: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 67: | Line 65: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File: | | [[File:BODgap_2.png|550px|thumb|left| Figure 2.Oil Damper with various gap lengths]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 76: | Line 74: | ||
'''References''': | '''References''': | ||
{| | {| | ||
| style="width:5px" | '''[1]''' || Akcelyan, S., | | style="width:5px" | '''[1]''' || Akcelyan, S., Lignos, D. G., Hikino, T. (2018). “Adaptive Numerical Method Algorithms for Nonlinear Viscous and Bilinear Oil Damper Models Subjected to Dynamic Loading.” Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 113, 488-502. [http://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2018.06.021]. | ||
|- | |||
| style="width:5px" | '''[2]''' || Akcelyan, S. (2017). "Seismic retrofit of existing steel tall buildings with supplemental damping devices." Ph.D. Dissertation, McGill University, Canada. | |||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Code Developed and Implemented by : <span style="color:blue"> '''''[http:// | Code Developed and Implemented by : <span style="color:blue"> '''''[http://sarvenakcelyan.com Sarven Akcelyan]''''' & '''''[http://dimitrios-lignos.research.mcgill.ca/PLignos.html Prof. Dimitrios G. Lignos]''''', (McGill University) </span> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:24, 19 July 2018
- Command_Manual
- Tcl Commands
- Modeling_Commands
- model
- uniaxialMaterial
- ndMaterial
- frictionModel
- section
- geometricTransf
- element
- node
- sp commands
- mp commands
- timeSeries
- pattern
- mass
- block commands
- region
- rayleigh
- Analysis Commands
- Output Commands
- Misc Commands
- DataBase Commands
This command is used to construct a BilinearOilDamper material, which simulates the hysteretic response of bilinear oil dampers with relief valve. Two adaptive iterative algorithms have been implemented and validated to solve numerically the constitutive equations within a bilinear oil damper with a high-precision accuracy.
| uniaxialMaterial BilinearOilDamper $matTag $K $Cd <$Fr $p> <$LGap> < $NM $RelTol $AbsTol $MaxHalf> |
| $matTag | integer tag identifying material |
| $K | Elastic stiffness of linear spring to model the axial flexibility of an oil damper (brace and damper portion) |
| $Cd | Viscous damping coefficient of an oil damper (before relief) |
| $Fr | Damper relief load (default=1.0, Damper property) |
| $p | Post-relief viscous damping coefficient ratio (default=1.0, linear oil damper) |
| $LGap | gap length to simulate the gap length due to the pin tolerance (default=0.0: zero tolerance) |
| $NM | Employed adaptive numerical algorithm (default value NM = 1; 1 = Dormand-Prince54, 2=adaptive finite difference) |
| $RelTol | Tolerance for absolute relative error control of the adaptive iterative algorithm (default value 10^-6) |
| $AbsTol | Tolerance for absolute error control of adaptive iterative algorithm (default value 10^-10) |
| $MaxHalf | Maximum number of sub-step iterations within an integration step (default value 15) |
Examples:
References:
| [1] | Akcelyan, S., Lignos, D. G., Hikino, T. (2018). “Adaptive Numerical Method Algorithms for Nonlinear Viscous and Bilinear Oil Damper Models Subjected to Dynamic Loading.” Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 113, 488-502. [1]. |
| [2] | Akcelyan, S. (2017). "Seismic retrofit of existing steel tall buildings with supplemental damping devices." Ph.D. Dissertation, McGill University, Canada. |
Code Developed and Implemented by : Sarven Akcelyan & Prof. Dimitrios G. Lignos, (McGill University)